Welcome to our latest blog post by HSE Documents, In our latest post, we look at the fascinating world of lifting operations with mobile cranes.
Mobile cranes play an important position in coping with heavy hundreds in industries which includes creation and production. The way we approach lifting tasks has been changed by these machines. The fundamental aspects of lifting operations with mobile cranes, as well as their various types, components, safety protocols, and the pivotal role they play in modern work environments, will be explored in this article. Whether you're a seasoned professional in the field or simply intrigued by the mechanics behind these engineering marvels, join us as we demystify the mechanics, challenges, and innovations that define the world of mobile crane operations.
We'll take you on a journey through the intricate planning that goes into each lift. Crane operators undergo rigorous schooling and certifications to ensure the proper well-being of all employees and the fulfillment of every operation.
We will be sharing real-life stories showcasing the incredible feats accomplished by mobile cranes. We will discuss how technology, such as remote operation and advanced sensors, is making crane operations even safer and more precise.
Whether you're here to expand your knowledge, gain insights into a dynamic profession, or simply marvel at the wonders of engineering and human ingenuity, our upcoming articles will offer a comprehensive look into the world of lifting operations with mobile cranes.
We are going to elevate your understanding of these heavy lifters and the role they play in shaping the modern industrial ecosystem.
1- Task
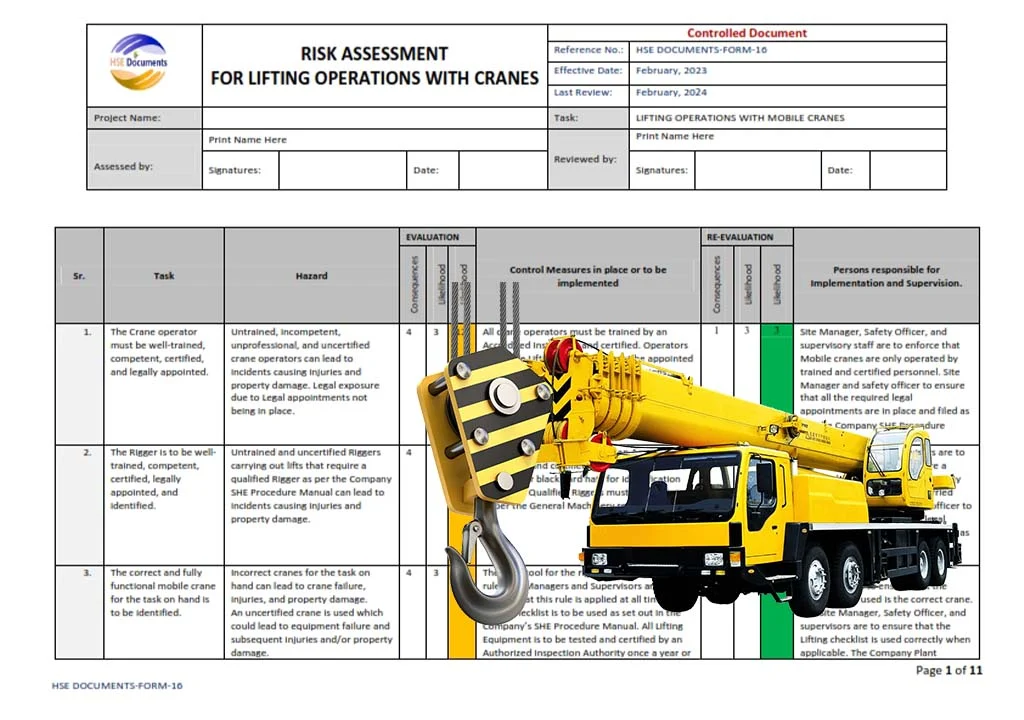
1. The Crane operator must be well-trained, competent, certified, and legally appointed.
2. The Rigger is to be well-trained, competent, certified, legally appointed, and identified.
3. The correct and fully functional mobile crane for the task on hand is to be identified.
4. Set up a mobile crane.
5. Obtain lifting equipment from the stores.
6. Slinging of load and attaching guide ropes.
7. Lift the load to the required elevation.
8. Slew load to position.
9. Lower the load very slowly into the correct position safely.
10. When in position, the lifting tackle slackened and was removed from the load carefully.
11. Return the lifting tackle to the designated area or store when all lifting tasks are completed.
12. Setting up the crane and using the crane for lifting the load.
2- Potential Hazard and Loss Exposure
1. Untrained, incompetent, unprofessional, and uncertified crane operators can lead to incidents causing injuries and property damage.
2. Legal exposure due to Legal appointments not being in place.
3. Untrained and uncertified Riggers carrying out lifts that require a qualified Rigger as per the Company SHE Procedure Manual can lead to incidents causing injuries and property damage.
4. Legal exposure due to Legal appointments not being in place.
5. Incorrect crane for the task on hand can lead to crane failure, injuries, and property damage.
6. An uncertified crane is used which could lead to equipment failure and subsequent injuries and/or property damage.
7. Unstable crane can tip over and lead to injuries and property damage.
8. Faulty lifting machinery can lead to injuries and damage.
9. No Rigging study is done which could lead to the overloading of the crane or other unforeseen events leading to subsequent failure of the equipment.
10. No qualified Rigger is used for all major lifts, the weight of the load is greater than 3 Tons or the volume/bulk, position, or surface area (wind resistance) of the load presents a degree of difficulty.
11. Overhead electrical cables can lead to electrocution.
12. The area is not barricaded off and/or no symbolic signs are used.
13. Environmental hazards caused by oil spillage.
14. Incorrect lifting tackle is obtained which could lead to equipment failure and subsequent injuries and damages.
15. Damaged equipment can lead to equipment failure.
16. Incorrect slinging methodology can lead to equipment failure and/or load failure.
17. No safe access is given to staff to gain access to the top of the load to carry out rigging & slinging operations. Their hands caught in a lifting tackle.
18. An unbalanced load could lead to lifting tackle failure and uncontrolled lift.
19. People walking under the load
20. The load can swing and collide with existing structures.
21. Guide ropes can come into contact with existing moving machinery in the area and lead to damage.
22. Instruction to crane operator are given by different people which could lead to confusion and have disastrous consequences.
23. Poor communication between the Rigger and the crane operator could lead to confusion, injuries, and property damage.
24. No safe access is given to employees to gain access to elevated areas where the load is to be positioned.
25. Employees awaiting the load are not aware of the position of the load.
26. Hand or body parts being injured due to employees coming between the load and its final resting place.
27. No safe access is given to staff to gain access to the top of the load to remove the lifting tackle Lifting tackle gets hooked when the crane repositions boom.
28. Tackle left lying around can lead to tripping hazards or equipment can be damaged.
29. Dragging of lifting tackle can lead to damage to equipment.
30. Oil Spillage. Atmospheric Emissions, Noise
3- Control Measures in place or to be implemented
1. All crane operators must be trained by an Accredited Institution and certified.
2. Operators of Mobile Lifting Equipment must be appointed as per the General Machinery regulations.
3. All Riggers must be trained by an Accredited Institution and certified.
4. All Certified Riggers are to wear black hard hats for identification purposes.
5. Qualified Riggers must be appointed as per the General Machinery regulations.
6. The right tool for the right job is the golden rule.
7. Site Managers and Supervisors are to ensure that this rule is applied at all times.
8. A lifting checklist is to be used as set out in the Company’s SHE Procedure Manual.
9. All Lifting Equipment is to be tested and certified by an Authorized Inspection Authority once a year or when repaired or modified.
10. This includes all integral parts of the said Lifting equipment e.g. hooks, crane rope, etc.
11. Each crane is to have its own Logbook as set out in the Companies SHE Procedure Manual.
12. The crane must be set up on stable ground and the outriggers fully extended.
13. If no suitable stable ground is available base plates are to be used to distribute the load.
14. A pre-use check is to be done on the crane by the operator and any faults must be reported to the Site Manager.
15. The pre-use checklist is to be kept with the operator for the period they are valid and then to be handed to the Safety Officer for the issue of a new checklist.
16. Rigging studies are to be done for all major lifts, the weight of the load is greater than 5 Tons or the volume/bulk, position, or surface area (wind resistance) of the load presents a degree of difficulty.
17. A qualified rigger is to be used for all lifts as specified in the Company’s SHE Procedure Manual.
18. In the case of small lifts a trained semi-skilled rigger/bank man can be used. It must be noted that as soon as a rigging study is required the lift is to be supervised by a qualified rigger.
19. The rigging crew must be competent and take note of all obstacles present in the immediate area where the lift is to take place.
20. When overhead power lines are present a Qualified Rigger must be present and a rigging study done.
21. Whenever any lifting operation is taking place the area is to be barricaded with black& yellow barricading tape and no entry signs are put in place.
22. The rigger or semi-skilled rigger is to ensure no one enters the area and none of his rigging team goes under the load.
23. The crane is to be checked every month by the appointed Lifting Equipment Inspector to ensure that there are no mechanical problems with the crane.
24. In the event of an oil spillage on the ground, it must be cleaned immediately after spillage and an oil drip tray or similar container is to be placed.
25. All Certified Riggers are to wear black hard hats for identification purposes.
26. Qualified Riggers must be appointed as per the General Machinery regulations must be in place to prevent further pollution. If on soil, the soil is removed to an approved designated area. If on concrete, the oil spill is soaked up with absorbent material or cleaned with a degreaser and then washed into the oil trap.
27. Only qualified Riggers or trained semi-skilled riggers/bank men are to book out rigging tackle.
28. All lifting equipment is to be inspected and certified annually by an Authorized Inspection Authority.
29. All lifting equipment is to be numbered and registered and is to be inspected monthly by the Appointed Lifting Tackle Inspector and color-coded as per the monthly color codes.
30. All users of lifting equipment are to do a pre-use inspection of the equipment before use.
31. Only qualified Riggers or trained semi-skilled riggers/bank men are to sling loads.
32. A ladder is to be used to obtain access to the top of the load. The use of PPE must be enforced at all times.
33. The correct lifting methodology is to be used by a competently trained rigging crew.
34. The rigger or semi-skilled rigger checks all rigging and lifts the load just off the ground to check for the balance of the load.
35. The area is to be barricaded off and no entry symbolic signs are to be used.
36. The Rigger or semi-skilled rigger is to use a whistle to warn everyone in the vicinity that the load is being lifted.
37. Guide ropes are to be used during lifting operations. In the case of piping or loads that due to their weight, shape, and/or surface area are prone to swing more than one guide rope is to be used.
38. Guide ropes are to be used under the direct instruction of the rigger or semi-skilled rigger.
39. Ensure that the guide rope is long enough so that it does not go into any moving machinery and is under control at all times or ensure that the load is lifted in such a manner that the guide rope cannot come into contact with any moving machinery.
40. Only the Rigger or semi-skilled rigger in charge of the lift is to give instructions to the crane operator.
41. The Rigger or semi-skilled rigger and the crane operator are to ensure that there is proper communication between them at all times.
42. If visible or electronic communication is interrupted, the crane operator is to stop operations until communication is re-established.
43. Employees are to gain safe access to elevated areas using existing safe access, scaffolding, or boatswain chairs.
44. The employees are then to use safety harnesses either attached to approved lifelines or a secure structure.
45. A rigger or semi-skilled rigger is to ensure that the employees awaiting the load are aware of its position before lowering it into position.
46. These employees are to use the guide ropes to control the load. Employees must ensure that they do not hold onto the load or climb onto it until it is in position.
47. Guide ropes are to be used. If the load is to be manhandled employees must ensure that they have no body part that can be jammed between the load and the surrounding existing structures.
48. Employees are to gain safe access to top off using existing safe access, ladder, or boatswain chair.
49. Employees at the load must ensure that the lifting tackle is properly disengaged and will not catch onto any item in the immediate facility before notifying the Rigger/semi-skilled rigger that the lifting tackle can be lifted. Employees are to ensure that lifting tackle does not get damaged due to working in haste.
50. Lifting tackle must be kept clean and stored on suitable hooks and shelves off the ground in a clean and dry area.
51. Employees are to ensure that lifting tackle is transported or carried in such a way that it will not damage the equipment.
52. All vehicles are to be serviced and maintained in good order to ensure that there are no oil leaks.
53. The Refillable cushions are to be used as soon as leakage is identified on the vehicle.
54. All vehicles are to be serviced and maintained in good order to limit exhaust emissions.
55. All vehicles are to be serviced and maintained in good order to ensure that the exhaust system is in good condition.
4- Persons responsible for Implementation and Supervision.
1. The Site Manager, Safety Officer, and supervisory staff are to enforce that Mobile cranes are only operated by trained and certified personnel.
2. Site Manager and safety officer to ensure that all the required legal appointments are in place and filed as per the Company SHE Procedure Manual
3. Site Managers and supervisors are to ensure that all lifts that require a qualified Rigger as per the Company SHE Procedure Manual are carried out.
4. Site Manager and safety officer to ensure that all the required legal appointments are in place and filed as per the Company SHE Procedure Manual
5. The Site Manager, Rigger, and Supervisor are to ensure that the mobile crane used is the correct crane.
6. The Site Manager, Safety Officer, and supervisors are to ensure that the Lifting checklist is used correctly when applicable.
7. The Company Plant Manager and site Manager are to ensure that these requirements are met before any Lifting Equipment is put into service.
8. The Site Manager, Safety Officer, Rigger, and supervisors are to ensure that cranes are stable before any lifting takes place. The site Manager and Supervisor are to ensure that the operators meet the requirements. The Site Manager, Safety Officer, and supervisors are to ensure that the control measures are adhered to.
9. Site Manager and Supervisors to ensure that this does not occur.
10. Supervisor and Rigger to plan the lift properly and communicate the procedure to everyone involved.
11. Site Manager, Safety Officer, Rigger, and supervisors to ensure that this is in place.
12. Site Manager, Safety Officer, Rigger, and supervisors to ensure that this is in place.
13. The Site Manager, Supervisor, and store manager are to ensure that this is complied with.
14. The site manager, Safety Officer, and Appointed Lifting Tackle Inspector are to ensure that this is complied with.
15. Site Manager, Riggers, and supervisors to ensure that control measures are adhered to. Site Manager, Rigger is to ensure that safe access is available and used.
16. The Site Manager, Safety Officer, and supervisory staff are to enforce the use of PPE by first educating staff and then disciplinary action if necessary.
17. Rigger, Semi-skilled riggers, and supervisors to ensure that loads are balanced before the lift takes place.
18. Riggers, semi-skilled riggers, and supervisors are to ensure that these measures are in place.
19. Rigger, semi-skilled rigger, and supervisors are to ensure the use of guide ropes.
20. Rigger/semi-skilled rigger, supervisor, and crane operators are to ensure that precautions are taken.
21. The rigger, semi-skilled rigger, and supervisors are to ensure that these measures are in place at all times.
22. Site Manager, Rigger is to ensure that safe access is available and used.
23. Rigger, semi-skilled rigger, and supervisors are to ensure that these measures are in place at all times.
24. Riggers, semi-skilled riggers, and supervisors are to ensure that employees are aware of the hazards.
25. Site Manager, Rigger is to ensure that safe access is available and used.
26. Rigger, semi-skilled rigger, and supervisors to ensure that all precautions are taken.
27. The Site Manager, Safety Officer, Riggers, Supervisors, and store man are to ensure that this is done. Rigger, semi-skilled rigger, and supervisors to ensure that all precautions are taken.
28. The Yard Manager is to monitor all company vehicles and ensure that they are in good working order.
29. Driver to ensure that he uses the cushions.
30. The Yard Manager is to monitor all company vehicles and ensure that they are in good working order.








No comments:
Post a Comment